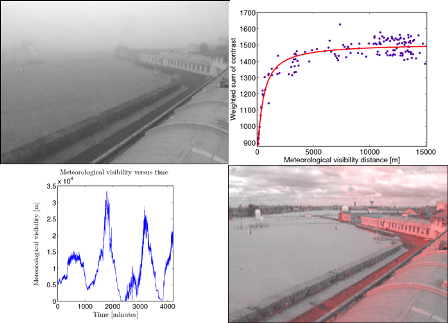
| Estimating the atmospheric or meteorological visibility distance is
very important for air and ground transport safety, as well as for air quality. However, there is no holistic approach to tackle the problem by camera. Most existing methods are data-driven approaches which perform a linear regression between the contrast in the scene and the visual range estimated by means of reference additional sensors. In this paper, we propose a probabilistic model-based approach
which takes into account the distribution of contrasts in the scene. It is robust to illumination variations in the scene by taking into account the Lambertian surfaces. To evaluate our model, meteorological ground truth data were collected, showing very promising results. This works opens new perspectives in the computer
vision community dealing with environmental issues. |
Publications- Babari, R., Hautière, N., Dumont, E. and Paparoditis, N. Mesure de la visibilité météorologique par imagerie : Une approche
modèle. In Congrès des jeunes chercheurs en vision par ordinateur (ORASIS'11),
Praz-sur-Arly, 2011.
  - Babari, R., Hautière, N., Dumont, E. and Paparoditis, N. a. J. Visibility Monitoring Using Conventional Roadside Cameras: Shedding
Light on and Solving Multinational Road Safety Problem. In Transportation Research Board Annual Meeting Compendium of Papers
(TRB'11), Washington, D.C., USA, 2011.
 - Babari, R., Hautière, N., Dumont, E. and Papelard, J.-P. a. N. Computer Vision for the Remote Sensing of Atmospheric Visibility. In IEEE/ISPRS workshop on Computer Vision for Remote Sensing of the
Environment, IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops,
Barcelona, Spain, pages 219-226, 2011.
 - Babari, R., Hautière, N., Dumont, E. and Paparoditis, N. Mesure robuste de la visibilité météorologique par caméra. In MajecSTIC 2010, Bordeaux, France, 2010.
 - Hautière, N., Babari, R., Dumont, E., Brémond, R. and Paparoditis,
N. Estimating Meteorological Visibility using Cameras: A Probabilistic
Model-Driven Approach. In Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV'10), Queenstown, New Zealand, pages 243-254, 2010.

|